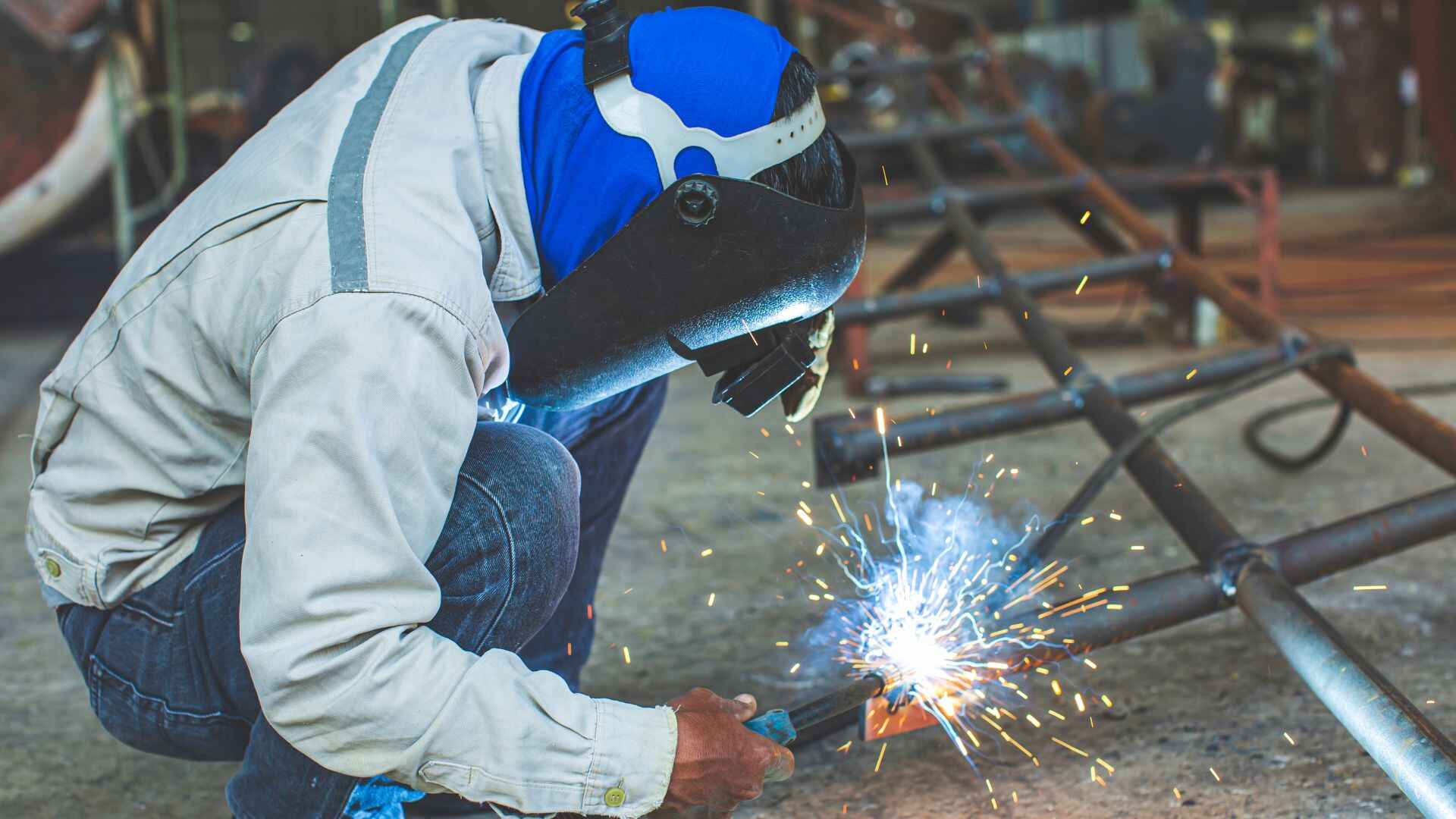
Different Types of Welding and Their Uses
Welding is a technical skill which is one of the most in-demand skills in Nepal and worldwide. It has a wide range of working industries, such as construction sites, hydropower projects, automobile workshops, and manufacturing. Welding is the process of joining metals and building strong structures. It is not just a skill; it is the transformation of your skills into career opportunities in Nepal and abroad for many youths.
If you are wondering how to acquire welding training in Nepal, first, you need to understand the different types of welding and their use cases. In this blog, we will discuss types of welding, career opportunities, and how you can choose the right training course based on your career goals.
What is welding?
This is the method of joining materials like metals, steels, and even thermoplastics by using heat, pressure, or both. It creates a permanent and strong bond.
It's commonly seen in Nepal, including:
• Projects like buildings, bridges and hydropower constructions.
• Workshops on automobiles and motorcycles.
• Metal fabrication shops.
• Industrial machinery and pipelines.
Why is welding an important skill in Nepal?
Every year in Nepal, the demand for welders is increasing in numbers. As Nepal is a developing country, Nepal has ongoing infrastructure development, hydropower projects, and the automobile sectors require trained welders. Having welding skills will increase the job potential for Nepalese in Gulf countries, Japan, Korea and even in Europe and offer attractive salaries.
After completing the welding training course in Nepal, you will be able to:
• You can work in local industries, workshops, and projects.
• It will open the door to apply for welding jobs abroad with higher income opportunities.
• Start a business of fabrication or workshop.
Types of welding and their uses.
Here are the most common types of welding methods, and their uses
1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW / Stick Welding)
This is one of the oldest and most widely used welding methods. It uses an electrode coated in flux to weld metals.
Uses:
• It is used in buildings and bridges.
• Pipelines and machinery’s repair and maintenance.
• Outdoor welding where portability is needed.
Training Level: Fundamentals of Welding
Many training institutes in Nepal start with SMAW because it is simple and cost-effective.
2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW / MIG Welding)
It is the process of welding by using a continuous wire electrode and shielding gas. It builds clean and efficient welds.
Uses:
• Automobile industry (car body repairs, fabrication).
• Sheet metal and light construction projects.
• Manufacturing workshops.
Training Level: Intermediate.
MIG is advanced than SMAW, and it requires more practice but is highly valuable in workshops.
3. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW / TIG Welding)
TIG welding is a precise welding technique that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and inert gas.
Uses:
• Welding stainless steel, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals.
• Hydropower projects, pipelines, and food industry equipment.
• Aerospace and high-precision industries.
Training Level: Advanced. TIG welding needs more control and skill, making it a valuable career skill for overseas jobs.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
This is a similar method to MIG welding; however, it uses a flux-filled wire. It doesn’t need external shielding gas, which is more reliable and practical for outdoor welding.
Uses:
• Heavy equipment manufacturing.
• Industrial construction projects.
• Outdoor welding where the wind makes MIG difficult.
Training Level: Intermediate.
This is the right choice for learners aiming to work in large industries.
5. Oxy-Acetylene Welding (Gas Welding)
This is a traditional welding technique that uses a flame of oxygen and acetylene gas. This is commonly used today in small workshops.
Uses:
• Repairing old machinery.
• Cutting and brazing metals.
• Workshop-level metal repairs in rural areas of Nepal.
Training Level: Beginner.
Often taught in training institutes as a base skill.
6. Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) (Advanced)
This welding is a high-tech method like TIG welding; the difference is that Plasma Arc is used for more precision.
Uses:
• Aerospace and defense industries.
• High-quality, small, and precise welds.
Training Level: Advanced. Rare in Nepal, but useful knowledge for students planning to work abroad.
Choosing the Right Welding Training in Nepal
Before joining a welding training institute in Nepal, you should consider the following:
• Hands-on practice: Check the course syllabus that provides practical training, not just fundamentals.
• Safety training: See the workshop that ensures safety protection
• Certification: Certifications like CTEVT or ISO will make you help you get a job in Nepal and abroad.
• Trainer experience: An expert trainer will help you learn in a better way.
Conclusion
Welding is a skill that builds the backbone of industries. From simple stick welding to advanced TIG and plasma welding, each type has its unique applications. For Nepalese youths, learning welding through proper training can open doors to secure local employment and high-paying jobs abroad.
If you are looking to build your skills in welding training in Nepal, you can explore our Welding training in Nepal.
Recent Post
-
 03 Feb 2025
03 Feb 2025How to Become a Plumber in Nepal
-
 11 Aug 2025
11 Aug 2025Common Digital Marketing Mistakes to Avoid
-
 12 Aug 2025
12 Aug 2025How to Become a Professional Video Editor
-
 13 Aug 2025
13 Aug 2025The Impact of AI on the Future of Graphic Design
-
 13 Aug 2025
13 Aug 2025How to Secure Your WordPress Site from Hackers
-
 14 Aug 2025
14 Aug 2025Common AC Problems and How to Fix Them
-
 14 Aug 2025
14 Aug 2025Career Opportunities in Motor Rewinding in Nepal
-
 18 Aug 2025
18 Aug 2025How to Plan and Install Industrial Wiring
-
 19 Aug 2025
19 Aug 2025Latest automobile technologies in 2025
-
 19 Aug 2025
19 Aug 2025Top Tools Every Motorbike Mechanic Need





